Multi-tenancy is a software architecture in which a single instance of a software application serves multiple customers, called tenants. In the context of Laravel, multi-tenancy refers to the ability of a Laravel application to serve multiple tenants, each with their own separate database.
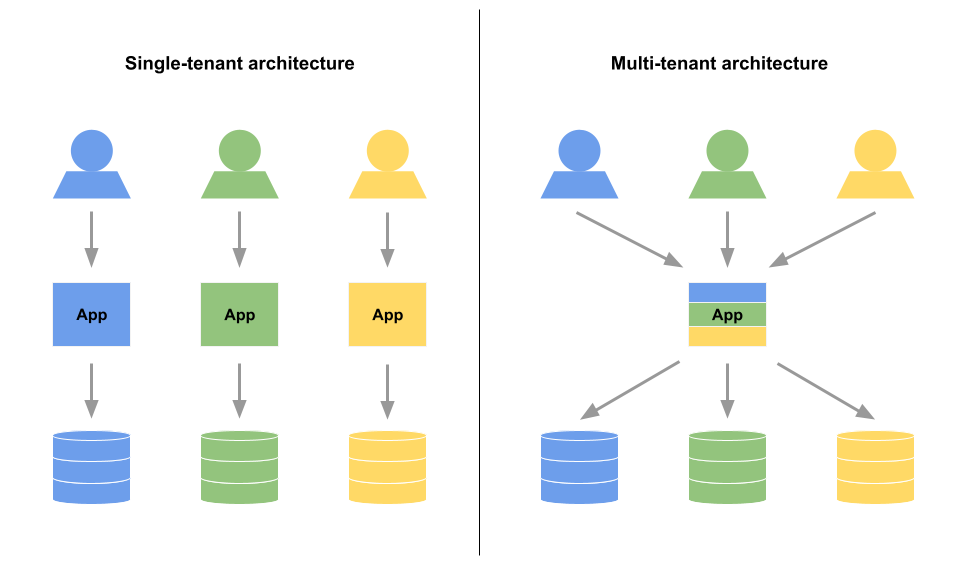
One way to implement multi-tenancy in Laravel is to use dynamic database connections. This involves setting up a database for each tenant and then switching between these databases at runtime based on the current tenant.
To set up dynamic database connections in Laravel, you will need to do the following:
- Set up a database for each tenant.
- Create a database connection for each tenant in your
config/database.phpfile. - Create a Tenant model to represent each tenant in your application.
- Use a middleware to switch the database connection based on the current tenant.
Set up a database for each tenant:
To set up a database for each tenant in a multi-tenancy application, you will need to do the following:
- Create a new database for each tenant. This can be done using a tool like PHPMyAdmin or the MySQL command line interface.
- Grant the appropriate permissions to the user that will be used to connect to the tenant's database. This will typically involve creating a new user and granting them access to the tenant's database.
- Update your Laravel application's
config/database.phpfile to include a connection for each tenant's database. - Here is an example of what the connections array in the
config/database.phpfile might look like for a multi-tenancy application with two tenants:
To create a new database using PHPMyAdmin, follow these steps:
- Open PHPMyAdmin in your web browser.
- On the left-hand side of the page, click the "Databases" tab.
- In the "Create database" field, enter the name of the database you want to create.
- Select the desired character set and collation from the dropdown menus.
- Click the "Create" button.
To create a new database using the MySQL command line interface, follow these steps:
- Open the MySQL command line interface.
- Connect to the MySQL server using the
mysql -u username -pcommand, replacing "username" with your MySQL username. - Enter your password when prompted.
- Create a new database using the
CREATE DATABASE database_namecommand, replacing "database_name" with the name of the database you want to create.
To grant permissions to a user in MySQL, you can use the GRANT command.
For example, to grant all privileges on a database to a user, you can use the following command:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON database_name.* TO 'username'@'localhost';This will grant the user with the username "username" all privileges on the database with the name "database_name".
You can also specify specific privileges instead of using ALL PRIVILEGES. For example, to grant a user select, insert, and update privileges on a database, you can use the following command:
GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE ON database_name.* TO 'username'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';To create a new user and grant them access to a database in one step, you can use the following command:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON database_name.* TO 'username'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';This will create a new user with the username "username" and the password "password", and it will grant the user all privileges on the database with the name "database_name".
Update your Laravel application's config/database.php file to include a connection for each tenant's database
To update your Laravel application's config/database.php file to include a connection for each tenant's database, you will need to add an array for each tenant's database to the connections array in the file.
The format of each connection array will depend on the type of database you are using (e.g., MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite). Here is an example of what a connection array for a MySQL database might look like:
'connections' => [
'tenant1' => [
'driver' => 'mysql',
'host' => 'localhost',
'database' => 'tenant1_db',
'username' => 'tenant1_user',
'password' => 'tenant1_password',
'charset' => 'utf8mb4',
'collation' => 'utf8mb4_unicode_ci',
'prefix' => '',
'strict' => true,
'engine' => null,
],
'tenant2' => [
'driver' => 'mysql',
'host' => 'localhost',
'database' => 'tenant2_db',
'username' => 'tenant2_user',
'password' => 'tenant2_password',
'charset' => 'utf8mb4',
'collation' => 'utf8mb4_unicode_ci',
'prefix' => '',
'strict' => true,
'engine' => null,
],
],Each tenant's connection array will have a unique key (e.g., 'tenant1' and 'tenant2'). The values in the array will specify the details of the connection, such as the driver, host, database name, username, and password.
Create a Tenant model to represent each tenant in your application.
In a multi-tenancy application, it is often useful to have a Tenant model to represent each tenant. The Tenant model can be used to store information about each tenant, such as the tenant's name, contact information, and database connection details.
To create a Tenant model in Laravel, you can use the following Artisan command:
php artisan make:model TenantThis will create a new Tenant model class in your application's app directory.
You can then define the attributes of the Tenant model by adding them as columns in the corresponding database table. For example, you might have a name column to store the tenant's name, a db_connection column to store the tenant's database connection string, and a contact_email column to store the tenant's contact email address.
Here is an example of what the Tenant model class might look like:
class Tenant extends Model
{
protected $fillable = [
'name',
'db_connection',
'contact_email',
];
}This model class defines the name, db_connection, and contact_email attributes as fillable, which means they can be mass-assigned using the model's create or update methods.
Use a middleware to switch the database connection based on the current tenant.
In a multi-tenancy application, you can use a middleware to switch the database connection based on the current tenant. The middleware will inspect the current request and determine the appropriate tenant based on some criteria (e.g., a tenant ID passed as a request parameter). It will then set the appropriate database connection for the request based on the tenant.
To create a middleware in Laravel, you can use the following Artisan command:
php artisan make:middleware TenantMiddlewareThis will create a new TenantMiddleware`` class in your application's app/Http/Middleware` directory.
You can then define the logic for switching the database connection in the middleware's handle method. Here is an example of how the handle method might look:
class TenantMiddleware
{
public function handle($request, Closure $next)
{
$tenant = Tenant::find($request->tenant);
if ($tenant) {
Config::set('database.default', $tenant->db_connection);
}
return $next($request);
}
}This middleware will find the current tenant based on the tenant request parameter (e.g., $request->tenant), and it will set the default database connection to the connection specified in the tenant's db_connection attribute (e.g., $tenant->db_connection).
You can then assign this middleware to routes that should use the tenant's database connection by adding it to the $routeMiddleware array in your application's app/Http/Kernel.php file.